Every year, thousands of road accidents carve permanent scars across South Africa, impacting lives and the economy.
Let’s dive into the complexities of road safety, exploring deep-rooted causes, personal stories, and innovative solutions that could turn the tide in our latest insightful article.
Background
Road safety in South Africa presents a complex challenge, marked by a higher incidence of traffic accidents compared to many other nations.
Each year, thousands lose their lives or are severely injured on the country’s roads, spotlighting a critical public health and safety issue that affects everyone—from daily commuters and pedestrians to long-distance truck drivers.
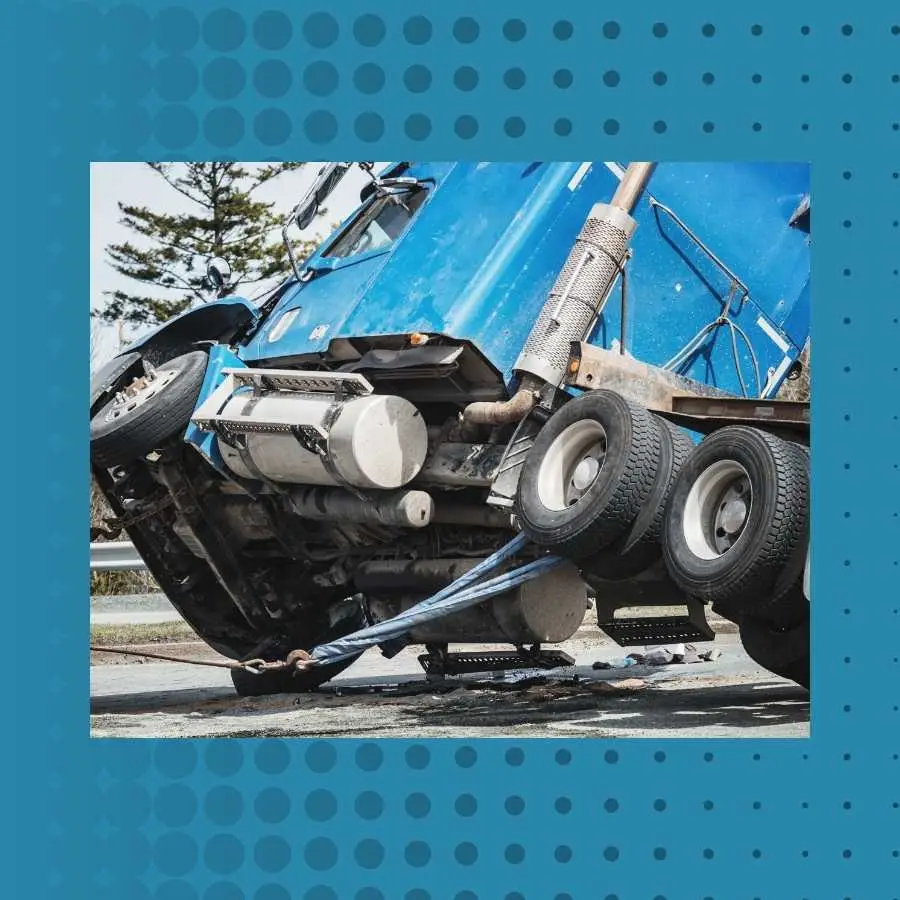

Addressing road accidents is not just about reducing statistics. Iit’s about saving lives and enhancing the quality of life for all South Africans.
It is also crucial for economic stability, as the aftermath of accidents imposes heavy costs on the healthcare system and impacts workforce productivity.
In this article, we will delve into the various factors contributing to road accidents in South Africa, examine the challenges faced in improving road safety, and explore effective measures and innovations being implemented to prevent accidents.
Through data-driven insights and compelling personal stories, we aim to foster a deeper understanding of the road safety landscape and encourage active participation in making South Africa’s roads safer for everyone.
Join us as we navigate the complexities of road safety, exploring the interplay of human behavior, legislation, infrastructure, and technology in shaping a safer future on the roads.
The Landscape of Road Accidents in South Africa
Understanding the Statistics
Road accidents in South Africa paint a troubling picture, underscored by high fatality and injury rates that rank among the worst globally.
In recent years, the statistics reveal a persistent challenge, with thousands of lives lost annually and many more affected by serious injuries.
Current Statistics on Road Accidents, Fatalities, and Injuries
According to the Road Traffic Management Corporation (RTMC), the past year has seen over 14,000 fatalities as a result of road accidents across the country.
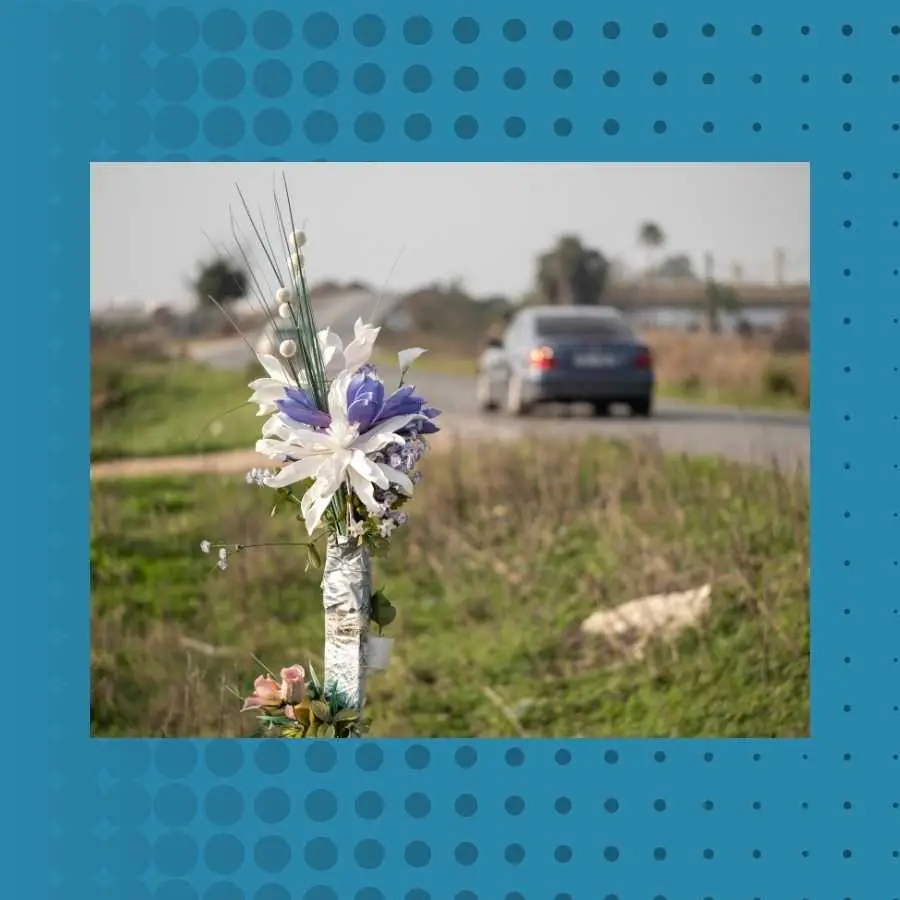

This alarming number is accompanied by an even higher count of injuries, many of which lead to long-term disability. These statistics not only highlight the human cost but also underscore the urgent need for comprehensive road safety strategies.
The distribution of these accidents is not uniform, with a significant proportion occurring on high-speed national highways and in urban areas during peak traffic hours.
Pedestrians remain disproportionately affected, accounting for nearly 40% of all road traffic deaths, a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities faced by non-motorized road users.
Trends Over the Past Decade
Looking back over the last ten years, the trends show a fluctuating pattern in road accident statistics, with some years witnessing slight declines, thanks to various road safety interventions.
However, these improvements have often been short-lived, followed by subsequent rises in accident rates.
For instance, after a notable decrease in fatalities due to heightened law enforcement and public safety campaigns, the following years saw a resurgence in numbers, pointing to the need for sustained and consistent safety measures.
Several factors contribute to these trends, including increases in vehicle registrations, urbanization, and varying levels of enforcement of traffic laws.

Economic fluctuations also play a role, as periods of economic downturn tend to see an increase in risky behaviors such as drunk driving and speeding.
This section has set the stage by providing a snapshot of the current state and historical trends of road accidents in South Africa.
As we proceed, we will explore the root causes of these accidents, the challenges in mitigating them, and the strategies that can potentially turn these statistics around.
Through this exploration, we aim to not only inform but also encourage proactive participation in road safety initiatives, reminding us that behind every statistic is a life deeply valued and sorely missed.

Primary Causes of Road Accidents
Understanding the factors that lead to road accidents is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. In South Africa, several key issues contribute to the high rate of road incidents, each compounding the challenge of ensuring safety on the roads.
Speeding: Its Prevalence and Impact on Safety
Speeding remains one of the most significant contributors to road accidents in South Africa. The allure of faster travel times often outweighs the perceived risks, but the consequences are undeniable.
Higher speeds reduce the driver’s reaction time and increase the severity of accidents.
The RTMC reports that excessive speed is responsible for approximately 30% of fatal road accidents. Areas with poorly enforced speed limits, particularly on rural roads and urban highways, see a higher incidence of speed-related accidents.
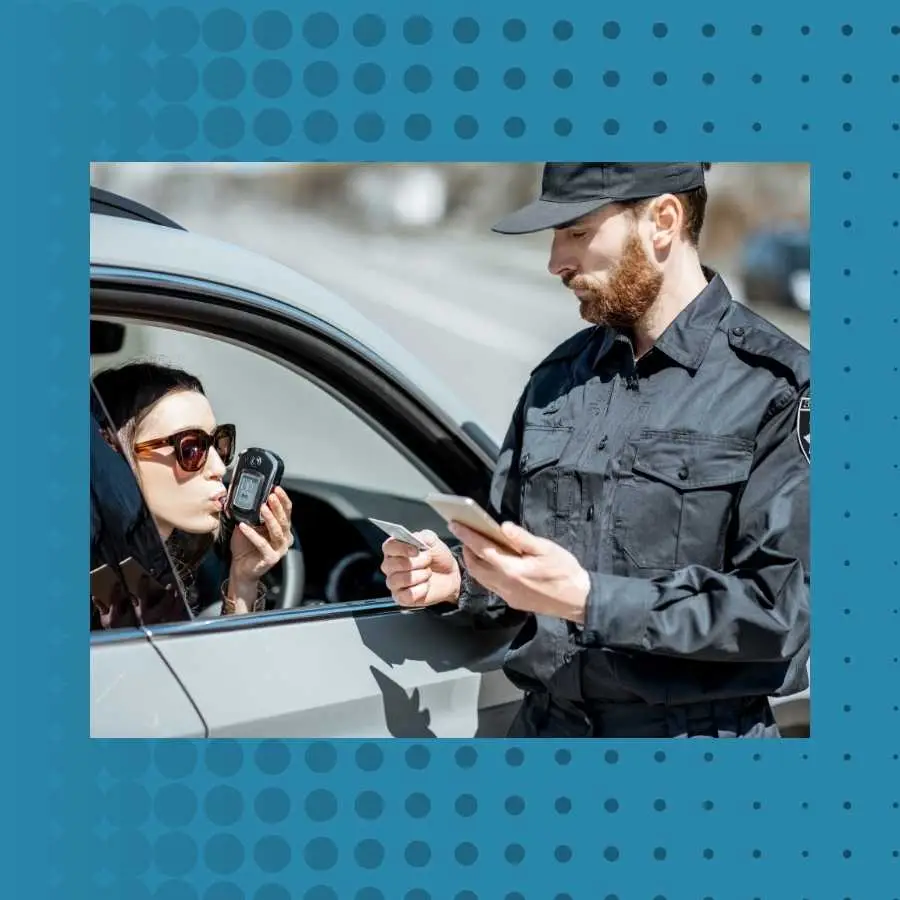
Influence of Alcohol and Drugs: Statistical Insights
Driving under the influence of alcohol and drugs drastically impairs judgment, coordination, and reaction times.
In South Africa, it is estimated that alcohol-related incidents account for up to 50% – 65% of all road fatalities.
These substances make it difficult for drivers to assess distances and react to sudden changes in traffic conditions, leading to an increased likelihood of collisions.
The legal blood alcohol concentration limit in South Africa is 0.05%, but enforcement varies widely, contributing to the prevalence of this issue.

Distracted Driving: The Role of Mobile Phones and Other Distractions
Distracted driving has emerged as a critical road safety challenge.
The use of mobile phones while driving, whether for texting, calling, or navigation, diverts attention from the road and significantly increases the risk of accidents. Other common distractions include eating, adjusting music or vehicle settings, and interacting with passengers.
The South African National Roads Agency has noted an increase in accidents attributed to distracted driving, especially among younger drivers.

Failure to Obey Traffic Signals: A Look at the Consequences
Ignoring traffic signals and signs is a dangerous practice that often leads to severe accidents, particularly at intersections.
Running red lights or failing to stop at stop signs can cause collisions that might involve multiple vehicles and result in significant injuries or fatalities.
Enforcement of traffic laws at intersections is crucial but remains a challenge in many parts of the country.

Reckless Driving Behaviors: Common Examples and Their Dangers
Reckless driving encompasses a range of risky behaviors that endanger the safety of all road users. These include aggressive driving, unsafe lane changes, tailgating, and not yielding the right of way.
Such behaviors not only increase the risk of collisions but also escalate minor incidents into serious crashes.
Public awareness campaigns and stricter penalties are vital for curbing reckless driving.

Vehicle Maintenance and Defects: How They Contribute to Accidents
The condition of a vehicle plays a crucial role in road safety. Defects such as brake failure, worn-out tires, and faulty lights can lead to catastrophic accidents.
Many vehicles on South African roads are poorly maintained due to economic constraints, leading to higher risks of mechanical failure. Regular vehicle inspections and maintenance are essential, yet compliance is inconsistent across the country.
Each of these factors illustrates a critical area where interventions are needed. By addressing these primary causes, South Africa can enhance road safety and significantly reduce the frequency and severity of road accidents.
The following sections will delve into the challenges of implementing these interventions and the strategies that have proven effective in other contexts.

Challenges and Solutions
Road Conditions and Infrastructure
The state of road infrastructure significantly influences the safety and efficiency of transportation.
In South Africa, where diverse landscapes and economic disparities affect infrastructure quality, the challenge of maintaining and improving roads is paramount.
Analysis of How Poor Infrastructure Contributes to Accidents
Poor road conditions, such as uneven road surfaces, potholes, and inadequate road markings, directly contribute to road accidents in South Africa. These conditions can cause drivers to lose control of their vehicles, lead to tire blowouts, or force drivers into oncoming traffic while trying to avoid obstacles.
Additionally, inadequate street lighting and poorly designed road layouts increase the risk of accidents, particularly at night and in adverse weather conditions.
Pedestrians, too, are at risk, with many roads lacking proper sidewalks or safe crossing points, contributing to the high pedestrian fatality rate.

Potential Improvements and Ongoing Projects
Addressing the issues of road safety through infrastructure requires comprehensive planning and significant investment. The South African government and various local authorities have initiated several projects aimed at improving road safety:
- Road Maintenance and Repair Programs: Ongoing maintenance projects aim to repair and resurface roads, fill potholes, and ensure that roadways are safe for all vehicles. Regular maintenance schedules are crucial to prevent the deterioration of road conditions that could lead to accidents.
- Upgrading Road Lighting and Signage: Improving the visibility on roads through better lighting and clearer, more reflective signage can significantly reduce accidents. Projects are underway in several provinces to install street lights and reflective road signs, especially at critical intersections and along rural roads.
- Redesigning Dangerous Intersections and Roadways: Some roads and intersections are notorious for high accident rates due to poor design. Redesigning these areas to include features like traffic circles, extended merging lanes, and improved sightlines can help reduce collision rates. Efforts are also being made to introduce traffic calming measures in residential areas to slow down vehicles.
- Enhancing Pedestrian Infrastructure: Building pedestrian bridges, improving crosswalks, and adding sidewalks are critical projects that help protect pedestrians, especially in urban centers and near schools. These improvements are vital in reducing the number of pedestrian casualties.
- Implementing Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS): ITS technologies, such as traffic sensors and automated traffic signals, are being explored to manage traffic flow better and respond to changing traffic conditions in real-time. These systems can help mitigate congestion-related accidents and improve overall road safety.
- Education and Community Involvement: Alongside physical improvements, there is a focus on educating the public about road safety. Community involvement projects are also part of the strategy, empowering local communities to take an active role in maintaining and monitoring their roads.
By continuing to invest in these improvements and integrating advanced technologies, South Africa can enhance its road infrastructure, significantly reducing the risk of accidents and improving the overall safety of all road users.
The commitment to ongoing evaluation and adaptation of strategies is essential to address emerging challenges and ensure the effectiveness of these initiatives.

Legislative Framework and Enforcement
Effective legislation and its enforcement are pivotal for ensuring road safety. South Africa has established a comprehensive set of traffic laws designed to mitigate accidents and encourage responsible driving behaviors.
However, the effectiveness of these laws greatly depends on consistent enforcement and public compliance.

Overview of Existing Traffic Laws and Regulations
South Africa’s road safety legislation encompasses a wide range of regulations, covering everything from speed limits and alcohol consumption to vehicle fitness and driver licensing.
The National Road Traffic Act and the associated Road Traffic Regulations provide the legal backbone, detailing the rules that all road users must follow. Key aspects of this legislation include:
- Speed Limits: Defined speed limits vary depending on the type of road and area (urban or rural). Enforcement through speed cameras and traffic police is intended to deter speeding.
- Alcohol and Drug Prohibition: Strict limits on blood alcohol levels for drivers, with penalties including fines, imprisonment, and license suspension for violations.
- Vehicle Standards: Regulations require that all vehicles on the road must pass a roadworthiness test to ensure they meet safety standards.
- Driver Licensing: A comprehensive system for issuing and renewing driver’s licenses, including testing for knowledge and practical driving skills.
- Seat Belt Laws: Mandatory use of seat belts for all vehicle occupants to reduce the risk of injury in accidents.

Challenges in Enforcement and Compliance
Despite these regulations, enforcement and compliance remain significant challenges. Factors contributing to these challenges include:
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources for traffic police and other enforcement agencies can lead to inadequate coverage, especially in rural and underserved areas.
- Corruption: Incidences of bribery and corruption within the traffic police can undermine enforcement efforts, allowing offenders to avoid penalties.
- Public Attitudes: Cultural attitudes toward certain laws, such as speed limits and drunk driving, may lead to widespread non-compliance unless there is a strong societal push for change.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient public education on new or existing traffic laws can lead to unintentional violations. Ongoing awareness campaigns are necessary to keep the public in

Impact of Legislation on Reducing Accidents
When effectively enforced, legislation has a significant impact on reducing road accidents. For example:
- Drunk Driving Laws: Enforcement of strict drunk driving laws has shown a correlation with reduced accident rates in areas with high visibility policing and frequent checkpoints.
- Speed Limit Enforcement: Studies have shown that in areas where speed limits are strictly enforced through the use of speed cameras and regular police patrols, accident rates have decreased notably.
- Helmet and Seat Belt Laws: Legislation requiring the use of helmets for motorcyclists and bicyclists, along with seat belts in cars, has been effective in reducing the severity of injuries from accidents.
To enhance the impact of legislation on road safety, South Africa needs to address enforcement challenges, ensure adequate resources and training for traffic officials, and cultivate a public ethos that respects and adheres to road safety laws.
Continuous monitoring and adaptation of laws to reflect new challenges and technological advancements are also crucial for maintaining relevance and effectiveness in improving road safety.

Safety Measures and Innovations
Promoting Road Safety
Improving road safety in South Africa is not solely about enhancing infrastructure or strengthening legislation. It also involves educating the public and integrating advanced technology to prevent accidents.
Both educational initiatives and technological innovations play critical roles in these efforts.
Educational Programs and Campaigns for Public Awareness
Educational programs and public awareness campaigns are fundamental in changing driving behaviors and promoting safety on the roads.
These programs are designed to inform drivers, pedestrians, and other road users about the dangers of irresponsible driving practices and the importance of compliance with road safety laws.
Key aspects include:
- School-Based Education: Integrating road safety into school curricula to teach children from a young age about the rules of the road and safe behavior as pedestrians and future drivers.
- Community Workshops: Conducting workshops in communities to discuss local road safety issues, proper pedestrian practices, and cyclist safety, especially in rural areas where road safety education may be lacking.
- National Campaigns: Launching high-visibility campaigns during holiday seasons and other high-risk periods to promote safe driving practices. Campaigns like “Arrive Alive” and “Buckle Up” have been successful in raising awareness and reducing accident rates during peak times.
- Media Involvement: Utilizing television, radio, and social media to reach a broader audience with messages about the dangers of drunk driving, speeding, and distracted driving.
These educational efforts are essential for fostering a culture of road safety that emphasizes personal responsibility and community involvement.

Role of Technology in Enhancing Road Safety
Technology plays an increasingly significant role in enhancing road safety, offering solutions that help prevent accidents and improve emergency responses.
Some of the key technological innovations include:
- Automated Enforcement Systems: Speed cameras, red-light cameras, and other automated systems are used to enforce traffic laws continuously without the need for police presence. These systems have been effective in reducing the incidence of speeding and red-light running.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Many new vehicles are equipped with technologies such as automatic braking, collision warnings, and lane-keeping assist, which help prevent accidents by compensating for human error.
- Traffic Management Systems: Intelligent traffic management systems use data analytics and real-time monitoring to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion-related incidents. These systems can adjust traffic signal timings based on current traffic conditions, improving road safety and efficiency.
- E-Enforcement and Mobile Apps: The development of mobile applications that allow citizens to report traffic violations and receive updates on road conditions can enhance community engagement in road safety efforts. Additionally, e-enforcement tools help authorities track and manage traffic offenses more efficiently.
The integration of these technologies, alongside traditional safety measures, provides a robust approach to preventing road accidents and enhancing the overall safety of road users in South Africa.
By continuing to innovate and educate, the country can achieve significant reductions in traffic-related injuries and fatalities, moving closer to a safer road environment for everyone.

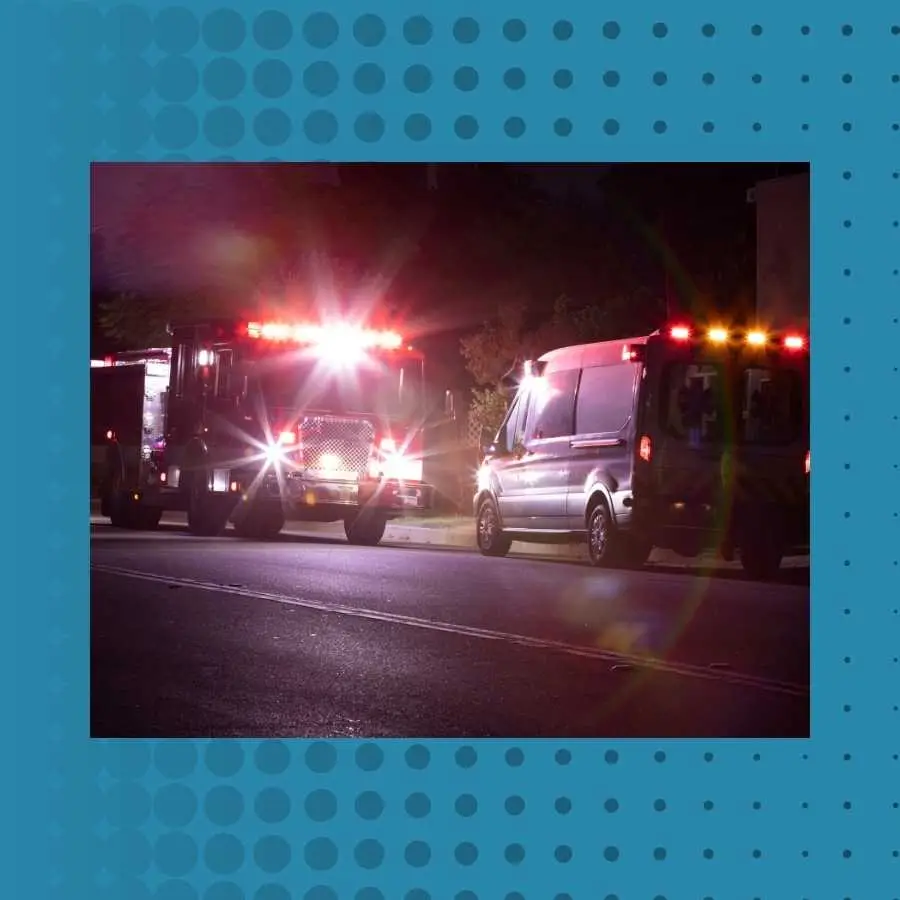
Emergency Response and Medical Care
Timely and efficient emergency response and medical care are crucial in reducing fatalities and improving outcomes for victims of road accidents.
In South Africa, where road accidents are a significant public health concern, the capacity to provide immediate and effective medical response can mean the difference between life and death.
Importance of Quick Response in Accident Scenarios
The first hour after a road accident, often referred to as the “golden hour,” is critical for the survival of accident victims.
Immediate medical intervention during this time can prevent death and limit long-term disability among survivors.
Quick response times:
- Reduce the Severity of Injuries: Rapid medical treatment can stabilize patients, prevent complications, and manage pain effectively.
- Increase Survival Rates: Immediate care ensures that life-threatening injuries are addressed as soon as possible, significantly increasing the chances of survival.
- Improve Long-Term Outcomes: Early intervention can also mean better recovery outcomes, reducing the long-term impact of injuries.
Efficient emergency response involves several components, including swift dispatch of emergency vehicles, skilled paramedics, and well-coordinated communication between the accident scene and hospitals.

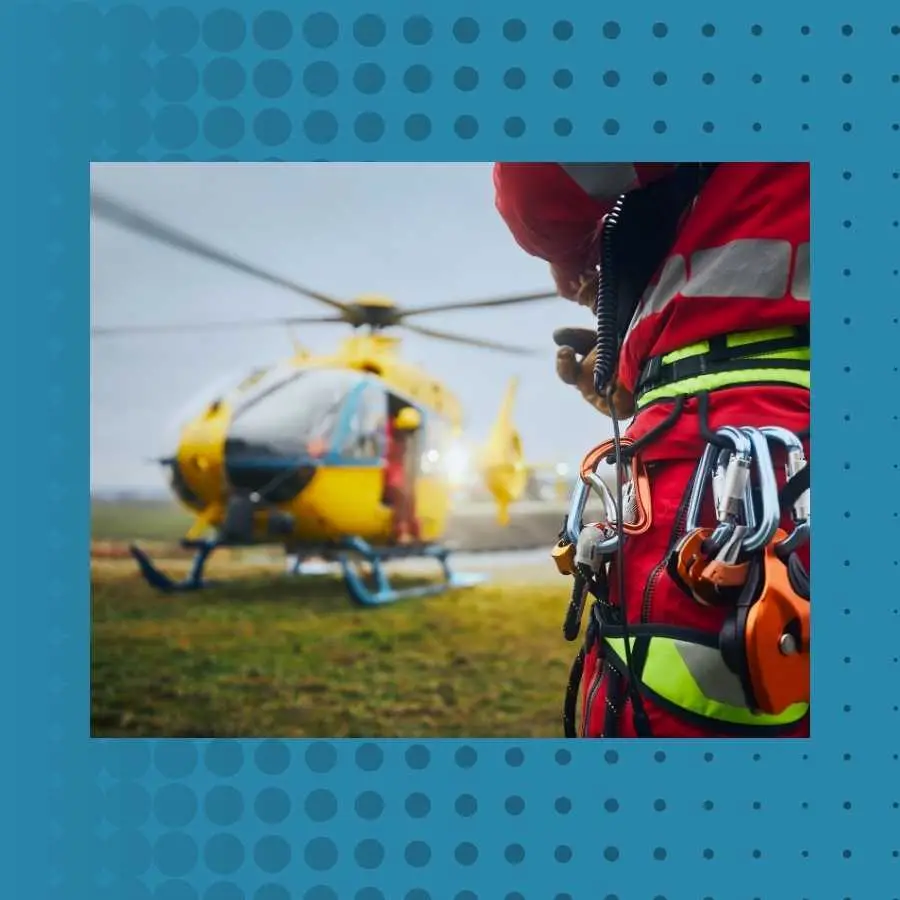
Facilities and Services Available for Accident Victims
South Africa has been developing its emergency medical services (EMS) to better cater to the needs of accident victims.
Key components of these services include:
- Ambulance Services: The country has a mix of public and private ambulance services that are equipped to provide on-site medical care and transport victims to hospitals. These services are crucial in areas far from medical facilities.
- Advanced Life Support (ALS) Units: Equipped with specialized medical equipment and trained personnel, ALS units offer more comprehensive care at the scene of an accident and during transport.
- Emergency Medical Centers: Major hospitals often have dedicated emergency departments equipped to handle severe trauma cases. These centers are staffed with specialists in emergency medicine and have the technology and facilities to provide advanced care.
- Helicopter EMS (HEMS): For critical cases, especially in remote or hard-to-reach areas, helicopter services can significantly reduce transport times to trauma centers.
- Trauma Counseling and Rehabilitation Services: Post-accident care also includes trauma counseling to help victims and their families cope with the psychological impacts of road accidents, as well as rehabilitation services to aid physical recovery.

Challenges and Improvements
While there are substantial services available, challenges remain in ensuring that these services are accessible to all South Africans, especially in rural or underserved regions.
Ongoing improvements in EMS include:
- Upgrading EMS Infrastructure: Increasing the number of ambulance bases and improving the distribution of resources across the country to ensure quicker response times.
- Training and Development: Continuous training for EMS personnel to handle a wide range of trauma situations effectively.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on how to react in an emergency, including basic first aid and how to contact emergency services, which is vital for improving the initial response to an accident.
Enhancing emergency response and medical care is a continual process that requires investment, innovation, and community involvement.
By strengthening these areas, South Africa can better protect its citizens and improve the prognosis for those affected by road accidents.
Economic and Personal Impact
Economic Burden of Road Accidents
The repercussions of road accidents in South Africa extend far beyond the immediate effects of the incidents themselves, permeating deep into the economic fabric of the country and affecting individual lives.
The financial implications of road accidents are substantial, involving direct and indirect costs that burden the economy and impact individuals and families.
The direct costs include emergency services, medical care, and law enforcement, while the indirect costs encompass lost productivity due to death or temporary and permanent disabilities resulting from accidents.
For individuals, the costs can be devastating, often involving prolonged medical treatment, loss of income, and the need for long-term care, which can drain family resources and savings.
The emotional and psychological toll on accident victims and their families further compounds these challenges, impacting their quality of life and ability to contribute economically.
Furthermore, road accidents significantly affect the insurance and healthcare sectors.
Insurance companies face high claims from accidents.
This, in turn, can lead to increased premiums for all drivers, affecting economic behavior and disposable income levels across the population. The healthcare sector is also heavily impacted, as hospitals and emergency services must allocate substantial resources to deal with the aftermath of road incidents.
This not only strains the healthcare system but also diverts resources from other critical health services.
The ongoing costs associated with road accidents underscore the importance of effective road safety measures and robust economic policies to mitigate these impacts.
By investing in road safety education, improving infrastructure, and enhancing emergency medical services, South Africa can reduce the frequency and severity of road accidents, thereby alleviating their economic and personal toll.
Such efforts are essential not only for safeguarding citizens but also for ensuring the economic stability of the country.

The Human Element
Behind the statistics and economic analyses of road accidents lies the human element, the deeply personal stories that resonate with the emotional and practical impact of road safety on everyday life in South Africa.
Each accident leaves a mark on the lives of individuals and communities, weaving a narrative of loss, resilience, and the urgent need for change.
Personal stories from accident survivors and families of victims often highlight the sudden and devastating changes they endure.
For instance, a father recounts the heartbreak of losing his young daughter to a speeding driver, a loss that shifts his world irrevocably, turning him into a fervent advocate for stricter speed enforcement.

A survivor of a serious accident shares the challenges of recovery, describing the long road to physical rehabilitation and the even longer journey to overcome the trauma and anxiety that persist long after the physical wounds have healed.
These stories underscore not only the physical damage caused by road accidents but also the enduring psychological scars they leave.
Moreover, road safety affects the fabric of daily life across the country. For many South Africans, the daily commute is fraught with hazards, from navigating poorly maintained rural roads to dealing with reckless driving in congested urban centers.

Parents worry about their children’s journey to school, particularly in areas where pedestrian infrastructure is lacking and where children must navigate dangerous traffic conditions on foot.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

The impact extends into the economy as well, where businesses feel the strain as employees recover from accidents or mourn lost colleagues.
These personal stories and experiences bring to light the pervasive impact of road safety issues.
They serve as a compelling call to action for policymakers, communities, and individuals to support and implement effective road safety measures.
They remind us that improving road safety is not just a matter of policy but a community imperative that can save lives and enhance the quality of life for all South Africans.
The Road Accident Fund: A Key Pillar in Road Safety Management in South Africa
The Road Accident Fund (RAF) plays a crucial role in South Africa’s approach to road safety, offering a safety net for those affected by road accidents. Established as a public entity, the RAF is tasked with providing appropriate cover to all road users within the country.
This involves compensating victims of road accidents for injury, loss of income, or death, without the need for lengthy and costly litigation.
Function and Impact of the Road Accident Fund
The RAF operates under principles that ensure victims of road accidents are compensated in a manner that is both fair and sustainable, helping to alleviate the financial burden associated with road accidents.
The fund covers various expenses, including medical costs, loss of earnings, funeral expenses, and general damages for pain and suffering. This comprehensive approach not only aids individuals and families in their recovery but also mitigates the broader economic impact by cushioning the financial blow that accidents can deliver to households.

Challenges Facing the RAF
Despite its critical role, the RAF faces significant challenges, primarily financial sustainability.
The fund has historically struggled with high liabilities and claims that outstrip its income, largely derived from a fuel levy. These financial challenges are compounded by administrative issues, such as delays in processing claims and disputes over the amounts awarded.
The result is often a backlog of cases and dissatisfaction among claimants who need timely support.
Reforms and Future Directions
Recognizing these challenges, there have been ongoing discussions and initiatives aimed at reforming the RAF to ensure its sustainability and improve service delivery.
Proposals have included the introduction of a new road accident benefit scheme that would work on a no-fault basis, potentially speeding up the compensation process and reducing administrative costs.
Such reforms are critical in maintaining the fund’s viability and ensuring that it can continue to serve its role effectively within the broader road safety management framework.
Integration in Holistic Road Safety Management
The RAF is an integral part of South Africa’s holistic approach to road safety.
While preventative measures are vital, the reality of existing road safety challenges makes it essential to have robust mechanisms in place for post-accident recovery and support.
The RAF complements legislative, educational, and infrastructure initiatives by providing a fail-safe that protects individuals financially in the event of accidents. This not only aids victims but also contributes to a safety culture by highlighting the real costs of road accidents to society.
While the Road Accident Fund has its challenges, its role in the fabric of road safety management in South Africa is indispensable. As the country continues to develop and implement comprehensive road safety strategies, ensuring the efficiency and sustainability of the RAF will be paramount.
This will require innovative solutions, reforms, and ongoing commitment from all stakeholders involved in road safety.

Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of road accidents and safety in South Africa, we have uncovered the multifaceted nature of this pressing issue.
From the alarming statistics that quantify the human and economic costs to the personal stories that give voice to individual experiences, it’s clear that road safety is a critical concern that affects all aspects of South African society.
The primary causes of these accidents—including speeding, alcohol and drug use, distracted driving, and poor vehicle maintenance—paint a complex picture of the challenges at hand.
Legislative frameworks and enforcement have their roles, but as we’ve seen, their effectiveness is often hampered by issues of compliance and corruption.
Technological advancements and educational campaigns offer promising avenues for improvement, enhancing both the enforcement of laws and the public’s compliance with them.

The importance of rapid and efficient emergency responses cannot be overstated, as these services are vital in reducing the severity of injuries and saving lives.
Yet, the economic and personal impacts of road accidents continue to burden individuals, families, and the nation as a whole, underscoring the need for comprehensive strategies to address road safety.
As we look to the future, there is a clear call to action for each member of society. Whether you are a driver, pedestrian, cyclist, or policymaker, your active participation in road safety initiatives is crucial.
By adhering to traffic laws, supporting road safety campaigns, and advocating for better infrastructure and policies, every South African can contribute to a safer road environment.
Together, through a collective commitment to change and the adoption of innovative solutions, we can achieve significant reductions in road accidents. It is our shared responsibility to ensure that the roads no longer represent peril but rather a safe passage connecting us to one another.
Let us move forward with a renewed focus on road safety, not only as a matter of policy but as a priority that protects and preserves the lives of all South Africans.
Ready to dive deeper into the Road Accident Fund ecosystem and stay ahead with the latest updates? Educate yourself on the vital aspects of road safety and support structures by subscribing to our newsletter.
Get informed, stay safe. Visit RAF Fact to subscribe now.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can speeding impact road safety in South Africa?
Speeding reduces a driver’s reaction time and increases the severity of accidents, making high-speed impacts more likely to result in serious injuries or fatalities.
What are the legal alcohol limits for drivers in South Africa, and why are they important?
The legal limit is a blood alcohol content of 0.05%. Keeping within this limit helps ensure that drivers can react quickly and make safe decisions on the road.
How does distracted driving contribute to road accidents?*
Distracted driving, such as using a phone or adjusting the radio, takes a driver’s attention away from the road, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
Why is it necessary to obey traffic signals?
Traffic signals manage the flow of vehicles and pedestrians, preventing collisions at intersections by ensuring that not all movements occur at the same time.
What constitutes reckless driving, and what are the risks?
Reckless driving includes aggressive behaviors like unsafe lane changes, speeding, and ignoring traffic laws, which can lead to unpredictable road conditions and accidents.
How do poor road conditions affect driver safety?
Bad road conditions, such as potholes and unclear road markings, can cause drivers to lose control or make sudden dangerous maneuvers, leading to accidents.
What role does technology play in enhancing road safety in South Africa?
Technology such as automated enforcement tools and advanced driver-assistance systems help prevent accidents by enforcing traffic laws and aiding in driver decision-making.
How do emergency response services improve outcomes after road accidents?
Quick and efficient emergency services can provide critical care within the golden hour after an accident, significantly improving the chances of survival and recovery for the injured.
What impact do road accidents have on the South African economy?
Road accidents cost the economy by increasing healthcare expenses, reducing workforce productivity due to injury or death, and elevating insurance premiums.
How can the general public participate in improving road safety?
Individuals can contribute by adhering to traffic laws, participating in road safety awareness programs, and using social media or community groups to promote and advocate for safer driving practices.
Glossary
- Automated Enforcement: The use of cameras and other technology to monitor and enforce traffic laws automatically without the need for human officers.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): In-vehicle technologies that help prevent accidents by supporting the driver in the driving process.
- Blood Alcohol Content (BAC): The percentage of alcohol in a person’s bloodstream, used to measure intoxication for legal and medical purposes.
- Golden Hour: The critical one-hour period after a traumatic injury during which medical treatment is most likely to prevent death.
- Helicopter EMS (HEMS): Emergency medical service using helicopters to transport critically injured patients quickly to treatment facilities.
- Intelligent Traffic Management Systems: Advanced systems that use data and technology to control the flow of traffic and improve road safety.
- Pedestrian Infrastructure: Facilities like sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian overpasses designed to ensure the safety of people walking.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives aimed at educating the public about various issues through media and public events to change public behaviors and attitudes.
- Traffic Congestion: A condition on road networks that occurs as vehicle use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queuing.
- Trauma Care: The specialized medical care provided for patients with severe and life-threatening injuries.
- Rehabilitation Services: Programs designed to help individuals recover from serious injuries, regain skills, or find new ways of performing tasks.
- Traffic Police: Law enforcement officers dedicated to enforcing laws regulating road traffic and motor vehicles.
- Vehicle Roadworthiness: The condition of a car that determines if it is suitable to be operated safely on public roads.
- Compliance: Adherence to laws or regulations governing road use, including traffic rules, vehicle standards, and safety regulations.
- Economic Impact: The effect of road accidents on a country’s economy, including costs related to healthcare, lost productivity, and legal expenses.






One Response
Thanks a lot for information